Installation
CCX is a comprehensive data management and storage solution that offers a range of features including flexible node configurations, scalable storage options, secure networking, and robust observability tools. It supports various deployment types to cater to different scalability and redundancy needs, alongside comprehensive management functions for users, databases, nodes, and firewalls. The CCX project provides a versatile platform for efficient data handling, security, and operational management, making it suitable for a wide array of applications and workloads.
Architecture Overview Diagram
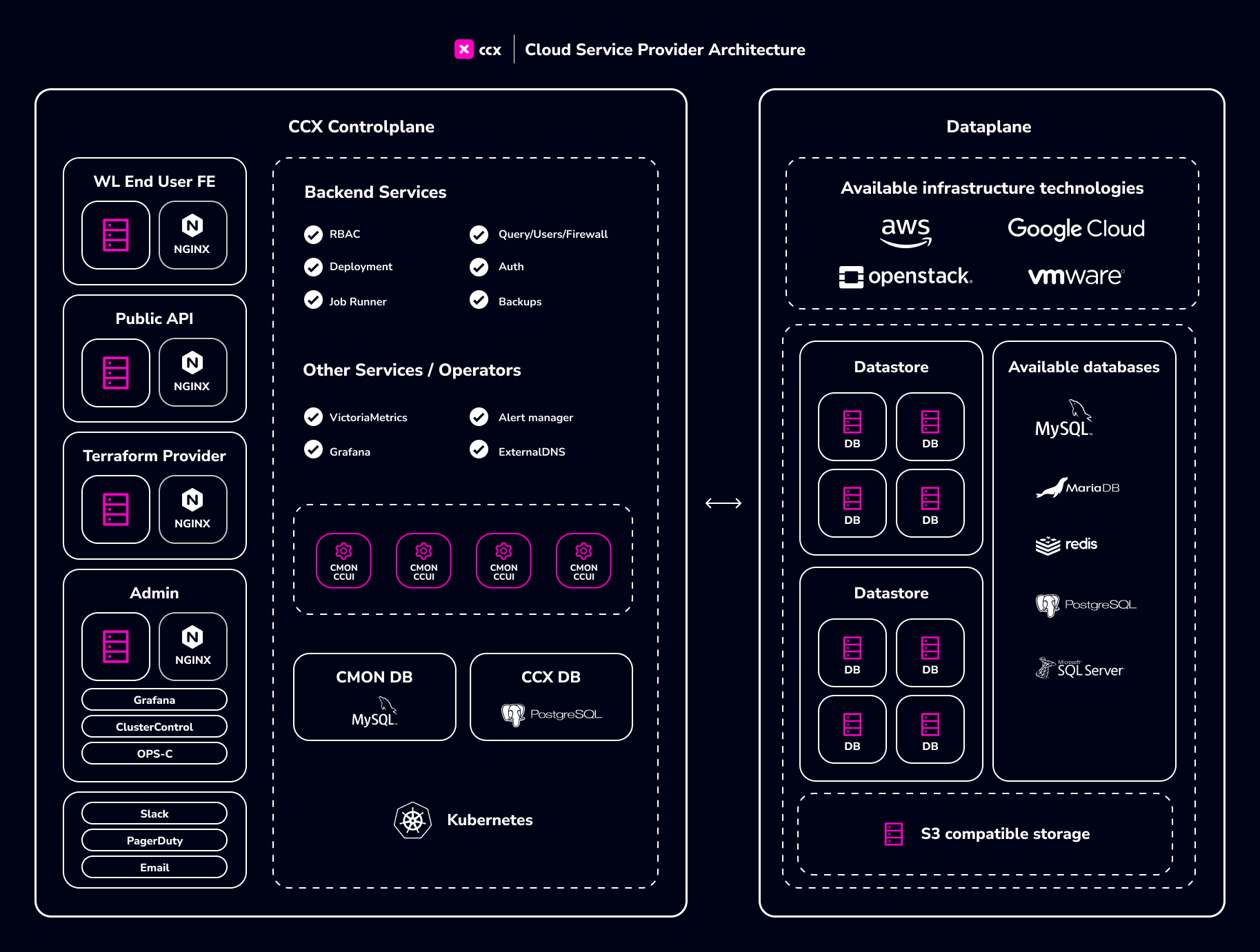
For a more details please read the architecture.
Quickstart
For laptop/desktop installation instructions please visit Install CCX on a Laptop.
Add Severalnines Helm Chart repository
helm repo add s9s https://severalnines.github.io/helm-charts/
helm repo update
Installation
# Install CCX dependencies
helm install ccxdeps s9s/ccxdeps --debug --wait
# Install CCX
helm install ccx s9s/ccx --debug --wait
If you do NOT have nginx ingress controller installed in your kubernetes cluster (very common in minikube or docker for desktop).You can install one that comes with ccxdeps chart like so:
# Install CCX dependencies
helm install ccxdeps s9s/ccxdeps --debug --wait --set ingressController.enabled=true
# Install CCX
helm install ccx s9s/ccx --debug --wait
Please note that this will install CCX on ccx.localhost.
Configuring your CCX installation
Providing cloud credentials
To be able to deploy datastores to a cloud provider (AWS by default) you need to provide cloud credentials. Cloud credentials should be created as kubernetes secrets in format specified in - https://github.com/severalnines/helm-charts/blob/main/charts/ccx/secrets-template.yaml
To setup cloud credentials for AWS (default provider) you can run the following one-liner:
# Create k8s secret from AWS credentials stored in ~/.aws/credentials
kubectl create secret generic aws --from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(awk 'tolower($0) ~ /aws_access_key_id/ {print $NF; exit}' ~/.aws/credentials) --from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(awk 'tolower($0) ~ /aws_secret_access_key/ {print $NF; exit}' ~/.aws/credentials)
Upgrade CCX to apply new config:
helm upgrade --install ccx s9s/ccx --debug --wait --set ccx.cloudSecrets[0]=aws
Setting up public access - custom domain name
Make sure that you have ingress controller in your cluster and you are able to setup externally facing load balancers and that either your domain name points to the ingress IP or you have external DNS configured in your cluster.
Simply run:
# Install CCX
helm install ccx s9s/ccx --debug --wait --set ccxFQDN=ccx.example.com
Further config
Please have a look at the helm values and minimal recommended values for CCX
- https://github.com/severalnines/helm-charts/blob/main/charts/ccx/minimal-values.yaml
- https://github.com/severalnines/helm-charts/blob/main/charts/ccx/values.yaml
Architecture Overview
A K8s Control plane responsible for the life-cycle of the datastores, backend databases and tools responsible for metadata such as users, datastores, and other resources.

Kubernetes cluster
K8s Control Plane Requirements
The control plane requires the following resources:
- 3 worker nodes
- 4vCPU Per node
- 8GB of RAM Per Node
- 60 GB of Disk (for PVCs)
Kubernetes Cluster version
CCX requires Kubernetes Cluster Version to be >=1.22.
Namespace
A namespace must be configured for the CCX K8s services to operate.
example: ccx
Helm Charts
The Helm charts are located in https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/severalnines/ccx. The source respository is located in https://github.com/severalnines/helm-charts. The three charts used below are:
- ccx
- ccxdeps
- observability
Prerequisite tool sets for CCX Installation
The following prerequisites are needed:
- nginx ingress controller
- NATS
- external-dns (Please see - DynamicDNS and please check the supported DNS provider for external-dns here). If you do not find your DNS on this list, we recommend that you create a zone in e.g AWS Route 53, CloudFlare or Google Cloud DNS.
- MySQL Database, aka CMON DB, is used by the CMON container to store metadata about managed/monitored data stores. See MySQL Operator installation guide.
- PostgresSQL Database, aka CCX DB, is used to store CCX (Control Plane) metadata. See Postgres Operator installation guide.
- Prometheus compatible monitoring server. If you don't have one, please visit the Observability installation guide.
This prequisite can be installed using ccxdeps. Dependencies required for CCX are created as child charts inside ccxdeps. By default only the ingress-nginx controller and the external-dns is not enabled in ccxdeps.
You can enable by setting it to true by using below command.
helm repo add s9s https://severalnines.github.io/helm-charts/
helm repo update
helm install ccxdeps s9s/ccxdeps --debug --set ingressController.enabled=true --set external-dns.enabled=true
Cloud Requirements
Flavors/images for datastores
CCX requires flavors built with Ubuntu 22.04 for the datastores. For a test/evaluation the following flavors are recommended:
- 2vCPU, 4GB RAM, 80GB Disk
- 4vCPU, 8GB RAM, 100GB Disk
Also, the easiest if there is a default login account called 'ubuntu' on the image.
Floating IPs / Public IPs
Create a pool of floating IPs (public IPs). Each VM requires a floating IP/public IP.
Disk Space
Disk space can either be ephemeral or block storage. We recommend block storage as block storage devices can be scaled.
Cloud Provider Configuration
To know more about the CCX Cloud Provider Configuration setup, please read CCX Cloud Provider Configuration.
Production Environment Configs
Backups needs to be configured for:
Danger
Severalnines is not responsible for backups that is lost or incorrect configuration.
Danger
Important Notice: Taking Persistent Volume Snapshots in Production Environment To ensure data integrity and availability in your production environment, it is crucial to take regular snapshots of Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) for CMON, DB's. Configure snapshot schedule at regular intervals, based on the criticality and update frequency of your data in your cloud environment